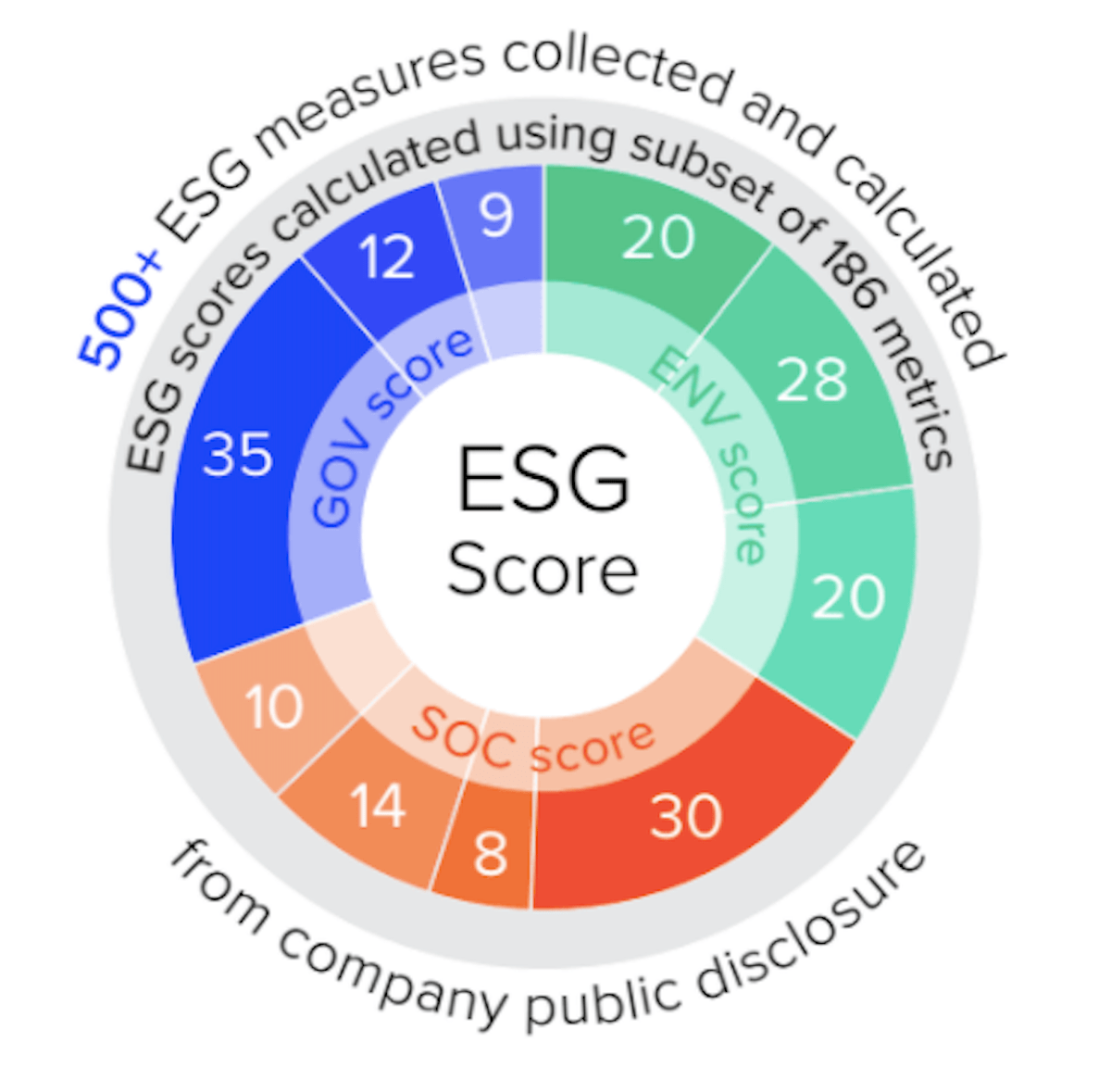
Introduction: Understanding ESG Scores
In recent years, environmental, social, and governance (ESG) considerations have gained significant traction among investors and businesses worldwide. ESG scores serve as a benchmark for evaluating a company’s sustainability performance and ethical practices. This article aims to shed light on what constitutes a good ESG score and why it is crucial in today’s business landscape.
The Importance of ESG Scores
ESG scores provide investors, stakeholders, and the public with valuable insights into a company’s commitment to sustainability, social responsibility, and corporate governance. These scores assess a company’s environmental impact, treatment of employees, diversity and inclusion practices, board composition, and more. A good ESG score demonstrates that a company operates ethically, reduces its environmental footprint, and prioritizes the well-being of its stakeholders.
Evaluating ESG Performance
To determine a company’s ESG score, various data points are considered, including but not limited to environmental emissions, labor practices, executive compensation, board independence, and supply chain management. Evaluating ESG performance involves assessing both quantitative and qualitative factors, such as carbon emissions reduction targets, employee satisfaction surveys, independent board evaluations, and community engagement initiatives.
Factors That Contribute to a Good ESG Score
A good ESG score is influenced by several factors. Companies that prioritize sustainable practices, implement robust corporate governance structures, foster inclusive workplaces, and actively engage with their communities tend to achieve higher ESG scores. Transparency in reporting and disclosing relevant ESG information is also a crucial element that contributes to a favorable score.
Industry-Specific Considerations
ESG considerations can vary across industries. For example, a technology company may focus on data privacy and cybersecurity, while a manufacturing firm may prioritize resource efficiency and waste management. Understanding industry-specific ESG challenges and tailoring strategies accordingly is vital for achieving a good ESG score that aligns with sector-specific standards and expectations.
ESG Score Methodologies
Several organizations and rating agencies provide ESG scores, each with its methodology and criteria. Common methodologies include assessing performance against international standards like the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) and Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB). Additionally, third-party research firms and indices evaluate ESG performance based on specific frameworks, such as the Dow Jones Sustainability Index or MSCI ESG Ratings.
Benefits of a Good ESG Score
Companies with good ESG scores enjoy various benefits. They attract responsible investors who prioritize sustainable investments, enhance their reputation and brand value, reduce operational risks, and create a positive impact on the environment and society. Moreover, a strong ESG performance can lead to increased access to capital, improved employee morale, and better relationships with regulators and other stakeholders.
Challenges in Measuring ESG Performance
Measuring ESG performance is not without its challenges. Data availability, comparability, and reliability can pose obstacles. Different industries may lack standardized ESG metrics, making it difficult to compare performance across sectors. Additionally, identifying material ESG factors and integrating them into investment decisions require comprehensive research and analysis.
The Role of Stakeholders in Promoting ESG
Stakeholders play a crucial role in promoting ESG practices. Shareholders can engage with companies through proxy voting and dialogues, urging them to improve their ESG performance. Customers can support businesses that align with their values, and employees can advocate for responsible workplace practices. Collaboration between companies, investors, policymakers, and civil society is essential to drive positive change and encourage widespread adoption of ESG principles.
Investor Perspective on ESG Scores
Investors increasingly consider ESG factors when making investment decisions. ESG scores provide investors with an indication of a company’s long-term sustainability and resilience. By incorporating ESG considerations into their investment strategies, investors can align their portfolios with their values and contribute to positive social and environmental outcomes.
Regulatory Landscape and ESG Reporting
Regulators worldwide are recognizing the importance of ESG and implementing frameworks to promote ESG reporting and transparency. Mandatory ESG disclosures are being introduced in various jurisdictions, requiring companies to report on their sustainability practices and risks. Compliance with these regulations is crucial for maintaining transparency and building trust with stakeholders.
ESG Integration in Business Strategy
Integrating ESG considerations into a company’s business strategy is essential for long-term success. Embedding sustainability principles into core operations, supply chains, and decision-making processes can drive innovation, risk mitigation, and value creation. Companies that effectively integrate ESG into their strategies are better equipped to adapt to evolving market demands and navigate future challenges.
The Link Between ESG and Financial Performance
Contrary to the misconception that ESG performance compromises financial returns, numerous studies have shown a positive correlation between good ESG scores and financial performance. Companies with strong ESG practices tend to attract investors, experience lower costs of capital, and demonstrate long-term resilience. Incorporating ESG considerations can lead to improved financial outcomes while contributing to a sustainable future.
Case Studies: Companies with Good ESG Scores
Several companies have achieved notable ESG scores, positioning themselves as leaders in sustainability and corporate responsibility. Examples include companies like Patagonia, known for their environmental stewardship; Unilever, recognized for their social impact initiatives; and Microsoft, renowned for their commitment to diversity and inclusion. These case studies showcase the positive outcomes of prioritizing ESG principles.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a good ESG score signifies a company’s commitment to sustainable practices, social responsibility, and strong corporate governance. Achieving a good ESG score involves integrating ESG considerations into all aspects of the business, engaging stakeholders, and adopting industry-specific standards.
As ESG gains prominence, companies that prioritize ethical and sustainable practices stand to benefit from enhanced reputation, access to capital, and long-term success.
FAQs
ESG scores are calculated using various data points related to a company’s environmental, social, and governance performance. These scores are determined by evaluating factors such as carbon emissions, labor practices, board independence, and supply chain management.
Yes, companies can improve their ESG scores over time by implementing sustainable practices, enhancing corporate governance, promoting social responsibility, and increasing transparency in reporting.
Yes, ESG scores are relevant to all industries, although the specific ESG factors and challenges may vary. Each industry has its unique considerations, and companies should tailor their ESG strategies accordingly.
ESG scores benefit investors by providing insights into a company’s long-term sustainability, resilience, and ethical practices. Investors can align their portfolios with their values and contribute to positive social and environmental outcomes.
Numerous studies have shown a positive correlation between good ESG scores and financial performance. Companies with strong ESG practices tend to attract investors, experience lower costs of capital, and demonstrate long-term resilience.